Summary of 7 regulations on electrical safety for enterprises
The following article will be provided by Galaxy M&E detailing 7 regulations on electrical safety for businesses in general and are included in Vietnam’s Electricity Law.
In 2004, the Government issued the Electricity Law with 10 chapters 70 articles applicable to organizations and individuals conducting electricity activities, using electricity or having other activities related to electricity in Vietnam. One of the important purposes of the Electricity Law is to ensure labor safety and prevent accidents caused by electricity. The following article will be provided by Galaxy M&E detailing 7 regulations on electrical safety for businesses in general and are included in Vietnam's Electricity Law.
I. INTRODUCTION OF ELECTRICITY LAW IN 2004
The Electricity Law of Vietnam was passed on the 3rd of December 2004 at the 6th session, National Assembly. By the 20th of November 2012, 25 articles out of 70 articles of the Electricity Law 2004 were amended and supplemented by the XIII National Assembly.
The amendments and supplements mainly concern organizations and units that carry out activities of production, transmission, distribution, dispatching of electricity systems, conduct electricity, market transactions, wholesale and retail electricity.
Out of 70 articles of the Electricity Law, 7 regulations on electrical safety apply to all individuals / organizations living in Vietnam. These regulations are concentrated in Articles 50, 51, 52, 53, 57, 58, 59 and are not within the scope of the amendments and supplements to Law No. 24/2012 / QH13.
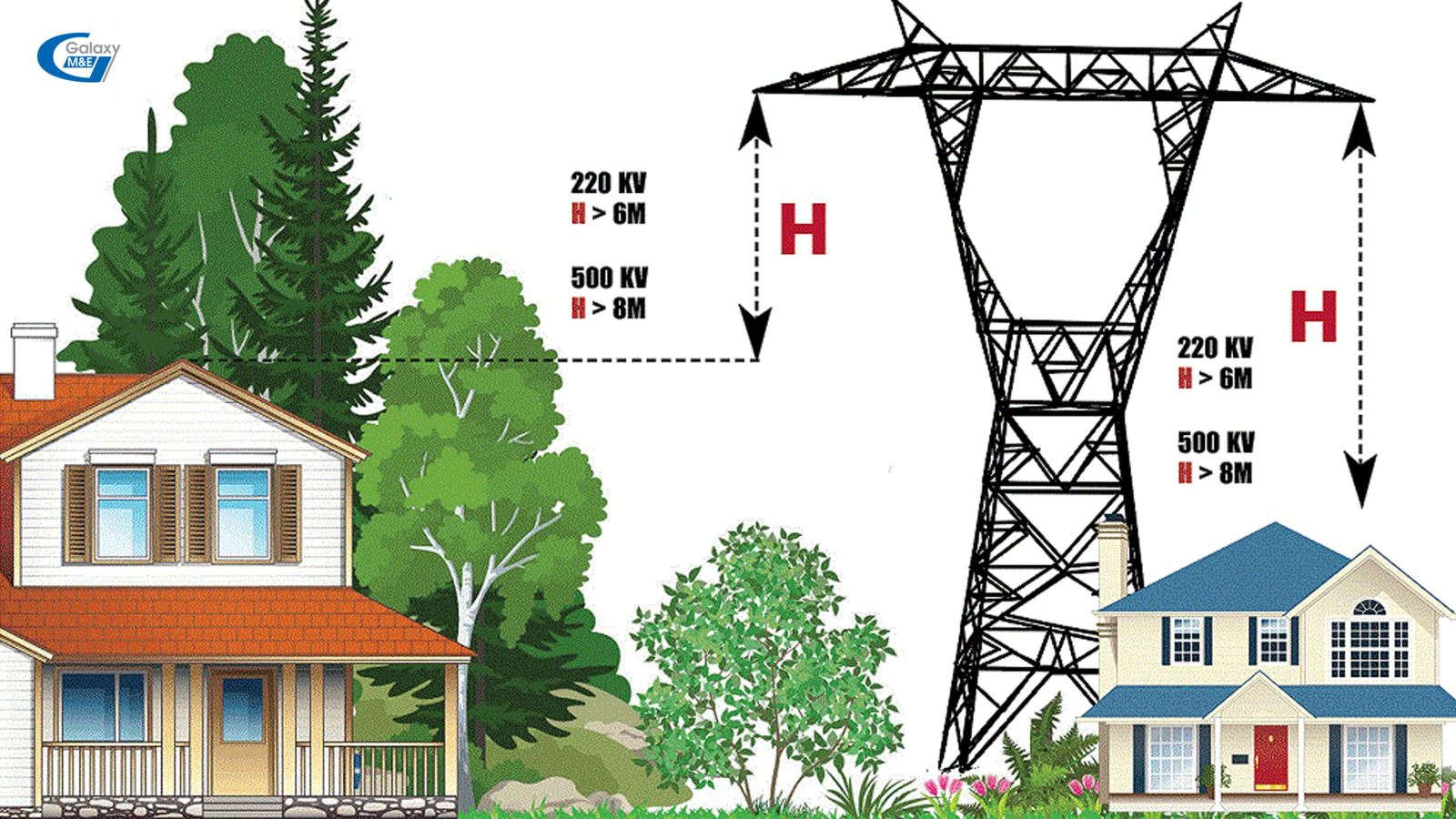
Safe distance between high-voltage lines and construction works.
II. REGULATIONS ON ELECTRIC SAFETY
Article 50. High-voltage electricity grid safety protection corridors
1. A high-voltage electricity grid safety corridor is the delimited space along an electricity transmission line or around a transformer station and specified according to voltage level.
2. The high-voltage electricity grid safety protection corridor includes:
a) The overhead electricity transmission line safety protection corridor;
b) The underground electric cable safety protection corridor;
c) The transformer station safety protection corridor.
3. The Government shall specify the high-voltage electricity grid safety protection corridors.
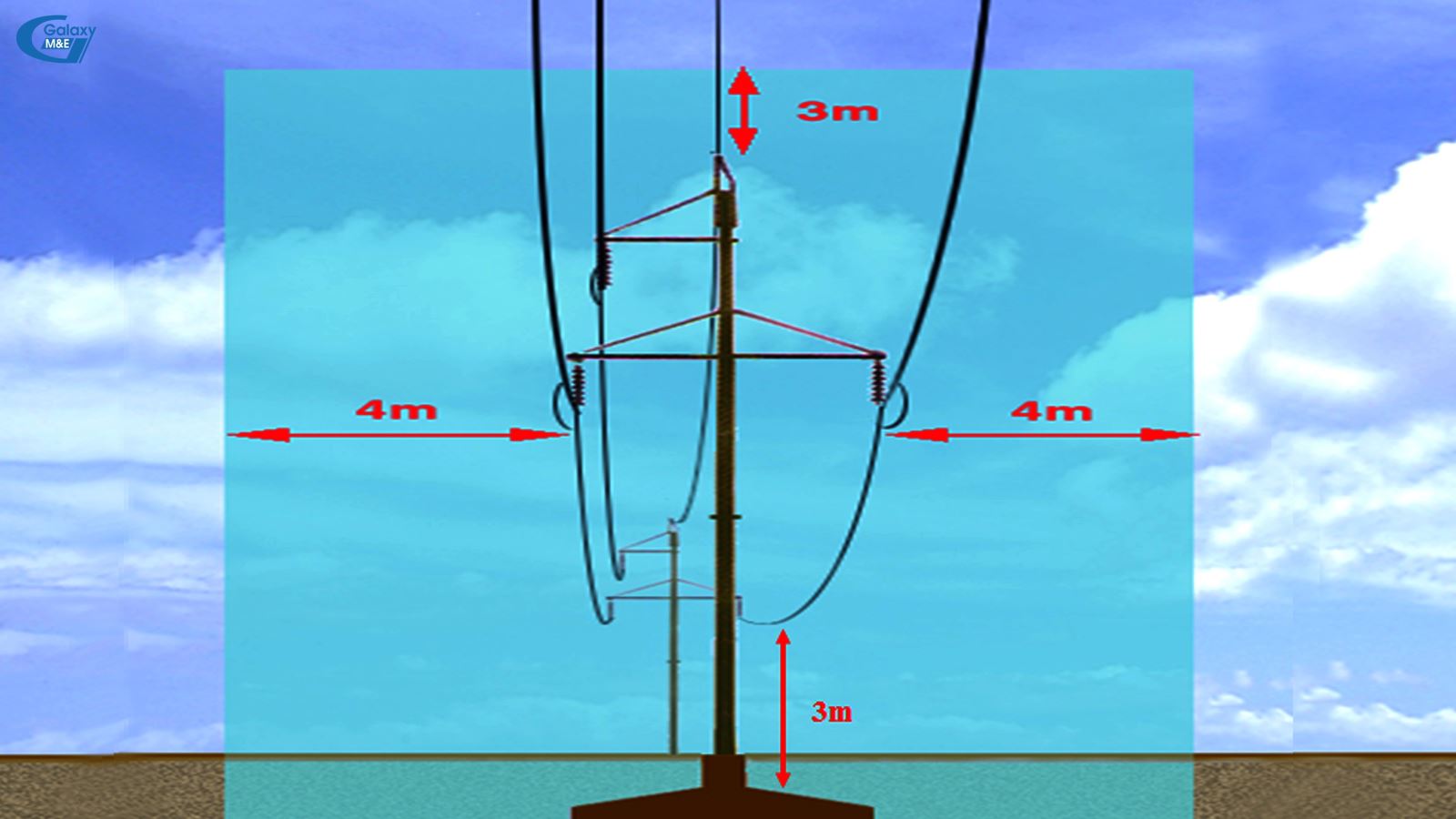
Safe distance to overhead power lines | Galaxy M&E
Article 51. Overhead electricity transmission line safety protection
1. Owners or users of dwelling houses or works, which are allowed to exist in the overhead electricity transmission line safety protection corridors must not use the roofs or any parts of such dwelling houses or works for purposes, which may encroach upon the electricity discharge safety distance according to the voltage grades and must comply with the regulations on protection of overhead electricity transmission line safety when repairing, renovating the dwelling houses or works.
2. Before granting permits to organizations or individuals for construction, expansion or renovation of dwelling houses or works in the overhead electricity transmission line safety protection corridors, the permit-granting agencies must request the investing owners of such dwelling houses or works to agree in writing with the high-voltage electricity grid-managing units on measures to protect the safety of the overhead electricity transmission lines and the safety in the course of construction, expansion, renovation and use of such dwelling houses or works.
3. Dwelling houses and works where people regularly live or work must not be allowed to exist in the safety protection corridors of the overhead electricity transmission lines of 500 kV or higher, except for specialized works in service of operation of such electricity grids.
4. All activities, if involving the use of equipment, instruments or means which may encroach upon the electricity discharge safety distance according to voltage grade, shall be banned from being carried out in overhead electricity transmission line protection corridors. In special cases where it is due to urgent defense or security requirements, agreement must be reached with the electricity grid- managing units on necessary safety protection measures.
5. At a cross-section between an overhead electricity transmission line and a land road or railway, the minimum height of the electricity transmission line at the lowest point when the line is in the state of maximum sagging is 4.5 meters plus the voltage-based electricity discharge safety distance. Where the highest points on the transport means are higher than the 4.5 meter-height, the means owners must contact the high-voltage electricity grid-managing unit for application of necessary safety measures.
6. At a cross-section between an overhead electricity transmission line and a railway reserved for electric trams, the minimum height of the transmission line at the lowest point when the line is in the state of maximum sagging is 7.5 meters plus the voltage-based electricity discharge safety distance.
7. At a cross-section between an overhead electricity transmission line and an inland waterway, the minimum height of the electricity transmission line at the lowest point when the transmission line is in the state of maximum sagging is equal to the overhead clearance height according to technical grade of the inland waterway plus the voltage-based electricity-discharge safety distance. The waterway transport means, when traveling through cross-sections between overhead electricity transmission lines and inland waterways must ensure that their heights shall not exceed the overhead clearance heights according to technical grades of such inland waterways. The safety distance of the overhead electricity transmission lines cutting across sea routes shall be specified for each specific case.
8. When carrying out activities on land or underground near or in the overhead electricity transmission line safety protection corridors, which may affect the normal operation of the transmission lines or threaten to cause electric incidents or accidents, the units carrying out such activities must reach agreement with the electricity work-managing units on necessary safety protection measures.
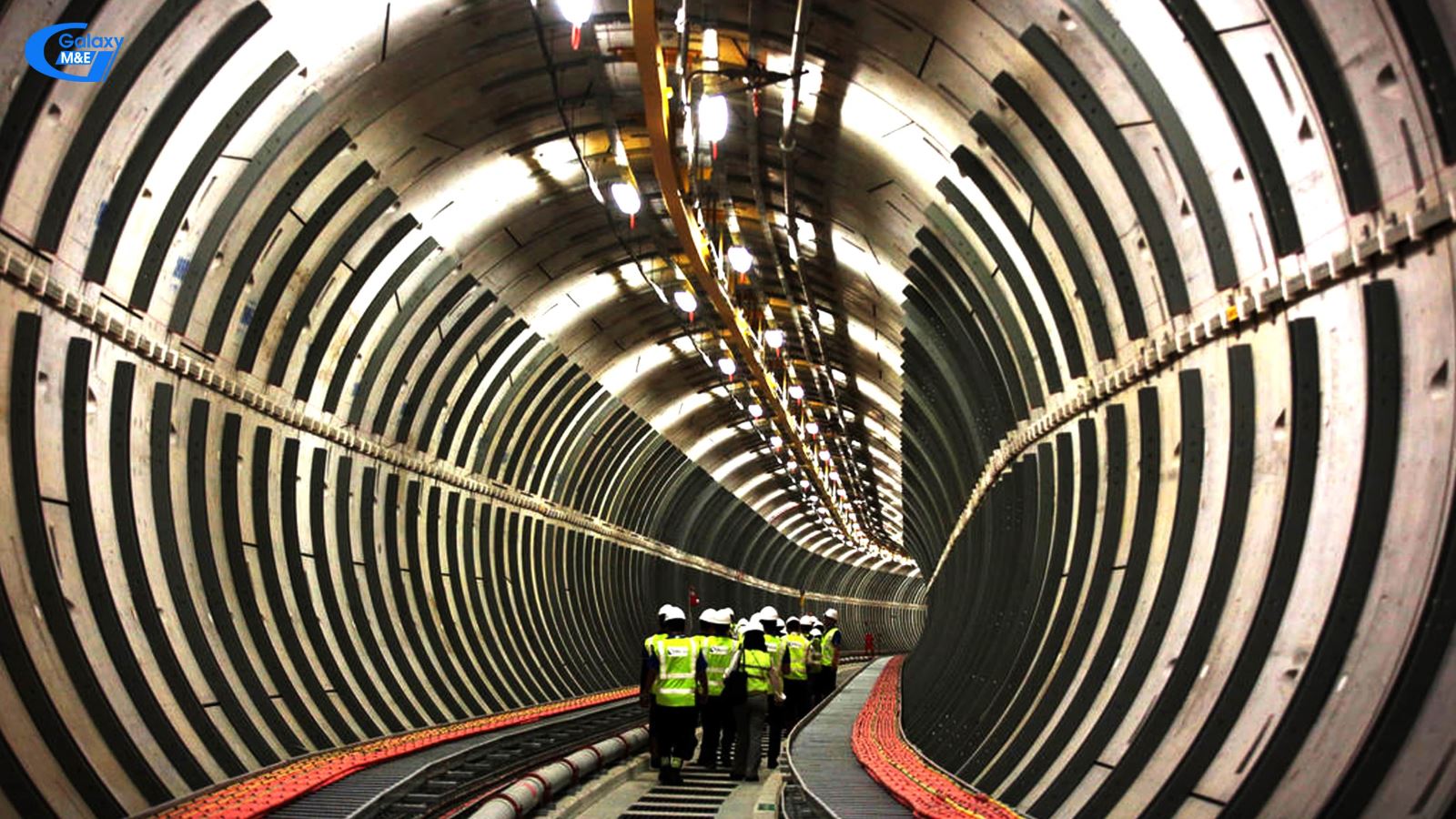

The underground transmission cable tunnel in Singapore is 40 km long, 6 m wide, 60 m to 80 m deep above sea level. They can hold 1,200 Km of high voltage cable. This system was built with the amount more than $ 2.4 billion | Galaxy M&E
Article 52. Underground electric cable safety protection
1. It is forbidden to dig holes, pile goods, drive piles, plant trees, build houses and other works, anchor vessels in underground electric cable protection corridors.
2. It is forbidden to discharge cable-corroding water and substances, equipment into underground electric cable protection corridors.
3. In case of discharging water and other substances outside the underground electric cable protection corridors, which may infiltrate, corrode and damage the cables, the owners or managers, users of dwelling houses or works from which such water or substances are discharged, shall have to handle them so as not to affect the cables.
4. When building works on land or dredging rivers, lakes within the underground electric cable protection corridors, the builders must notify such to the electricity work-managing units at least ten days in advance and must apply measures to protect the safety of the underground electric cables.
Article 53. Transformer station safety protection
1. Not to build dwelling houses, works or to plant trees of over two meters high in the transformer station safety protection corridors; not to encroach upon the walk-ins and walk-outs of transformer stations.
2. Dwelling houses or works built near transformer station protection corridors must ensure not to damage any parts of the stations.

Signs warning electric accidents according to international standards | Galaxy M&E
Article 57. Safety in use of electricity for production
1. Organizations and individuals using electricity for production must comply with the regulations on electric safety, regulations and technical standards on electric safety must conform with Vietnamese standards.
2. Electric equipment, systems of electric equipment, lightning-arresting and earthed systems must be pre-acceptance tested, periodically and extraordinarily checked according to the electric safety regulations and technical standards. The diagrams of these systems must be compatible with actual positions and be archived together with inspection minutes throughout the course of operation.
3. The internal transformer stations, high-voltage equipment and transmission lines must be installed and managed according to electric safety regulations and technical standards.
4. Electric equipment must conform to “Vietnamese Standard - Low-Voltage Electric Equipment - General Requirements on Protection against Electric Shocks” and “ Vietnamese Standard - Regulations on Earth-Connection and Air-Connection of Electric Equipment” to prevent electric shocks.
5. Electricity transmission lines, electric conductors must be designed and installed to ensure clear and airy production ground, thus avoiding mechanical or chemical impacts with may cause breakdowns. Metal structures of workshops, machinery, metal tubes must not be used as “neutral conductors,” except for special cases where separate designs approved by competent state bodies are required.
6. The electric systems in areas where exist inflammables, explosion-prone substances must be designed, installed and used according to the provisions of Clause 4, Article 54 of this Law.
6. Electric equipment used in minerals exploitation, electric instruments, mobile electric equipment, welding machine, electrolysis, electroplating equipment must conform to the relevant electric safety regulations and technical standards.
Article 58. Safety in use of electricity for daily-life and service activities
1. The total output of electric equipment used in offices, daily-life and service activities must conform to the designed capacity; the cross-sections and insulation durability of electric wires must conform to technical standards.
2. Heat-emitting electric equipment must not be placed near things easy to catch fire or to explode.
3. Electric equipment must be checked and maintained according to regulations, satisfy the electric safety technical standards and not cause dangers to users.
4. Electricity-using organizations and individuals shall have to organize the examination of safety of their respective electric systems, detecting and preventing in time dangers of electric incidents or accidents.
5. Low-voltage electricity grids shall be built only after their designs are approved.
6. Electric branch lines conducting electricity to dwelling houses, works must satisfy electric safety conditions, ensure beautiful look and not hinder activities of traffic means, ambulances, fire-fighting engines.
7. In three-phase four-wire electric circuits, automatic circuit breakers, switches, fuses and other circuit-breaking equipment must not be connected to the neutral wires.
8. In one-phase two-wire electric circuits, fuses and switches must be connected to the phase wire, but not to the neutral wire. Automatic circuit breakers and two-pole knife-switches are encouraged to be installed so as to simultaneously switch on/off of two wires.
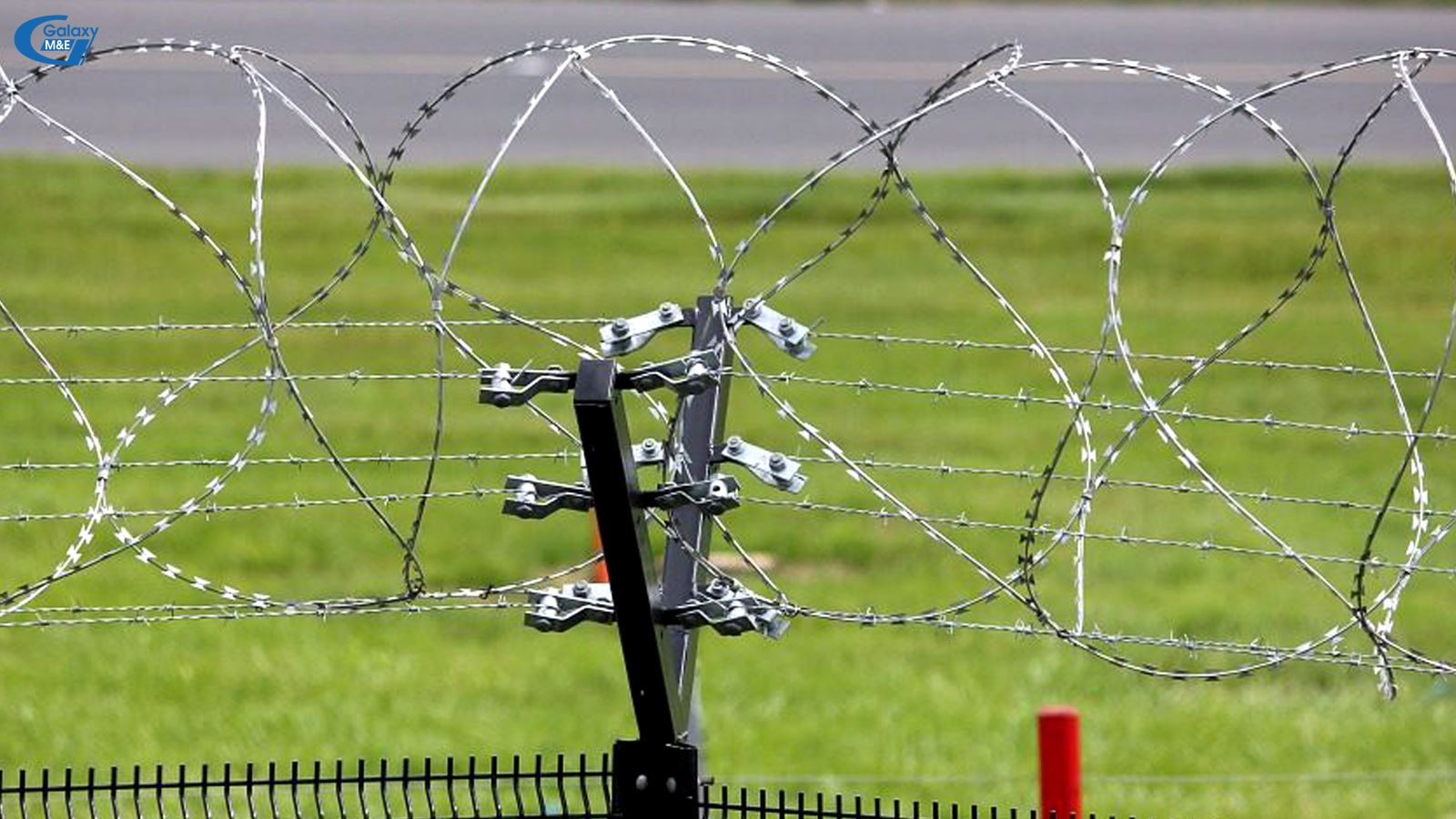

Electric fences are often used for security and defense purposes | Galaxy M&E.
Article 59. Using electricity as direct protection means
1. Using electricity as a direct protection facility means the use of electric source with appropriate voltage for direct connection with fences, barriers or shields of protected areas (hereinafter referred collectively to as electric fences) in order to prevent the infiltration into the protected areas and to emit alarming signals to persons guarding such areas.
2. Electricity shall be used as a direct protection means only when other protection measures have been applied inefficiently, and such must be permitted by competent state agencies.
3. Electric fences must be designed and installed to avoid all accidental contacts with people and cattle, to have danger signboards, not to affect the operation of electric system and not to cause danger to vicinities and living environment. The electric fence managers and users must be professionally trained in electricity.
4. The Minister of Public Security, the Minister of Defense shall, within the ambit of their respective tasks and powers, prescribe areas permitted for use of electric fences.
5. The Industry Minister shall prescribe standards and conditions for using electricity as direct protection means.

All regulations on construction, operation, use, repair, etc. of electro-mechanics are aimed at employees' safety goals | Galaxy M&E.
III. OTHER DOCUMENTS RELATED TO ELECTRIC SAFETY
In addition to the contents specified in the Electricity Law 2004, the Government also issued a number of documents guiding the implementation of the Law, detailed regulations of distance the safety discharge and conditions for dwelling houses in the grid protection corridor, regulations on electricity safety training …
For businesses, in addition to Government documents, there are additional specific policies to concretize the contents of the Electricity Law. These policies are designed based on the characteristics of the business and production of the business and together aim to improve the quality of electrical works, ensure absolute safety for people and property of the unit as well as of organizations and individuals concerned.
In order to help minimize the risk of electrical accidents, each organization or individual needs to equip themselves with knowledge related to electrical safety. Absolutely do not participate directly in the operation and repair of electrical equipment without mechanical and electrical expertise.