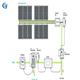
6 regulations regarding electrical safety training
As a unit specializing in consulting, designing and constructing of mechanical and electrical works with the desire to create safety and have sustainable values for customers, Galaxy M&E would like to send to readers a detailed copy of regulations that one should follow in their homes, countries regarding electrical training, ranking and issuance.
Occupational safety and prevention of electrical accidents is always a matter of concern for businesses and workers. Unlike mechanical accidents, the risks of electrical accidents are difficult to detect through hearing and sight. Electrical accidents are only known when incidents occur due to the contact of a charged material. In order to avoid the risk of electrical incidents and accidents from occurring, employers and individual workers need to attend training courses on electricity safety and incident prevention.
The organization of safety training courses for workers and electricity users is simple but the quality and content of the courses are still questionable. This exists due to the failure to fully understand the Government regulations, training curriculum framework, training content, and conditions for issuing electricity safety cards. Although the search of Government documents regulating labor safety and preventing accidents caused by electricity is easy, not all individuals and organizations actively learn. As a unit specializing in consulting, designing and constructing of electrical and mechanical works with the desire to create safe and sustainable values for customers, Galaxy M&E would like to send to readers the detailed regulations of the Government regarding training, ranking and issuance of electrical safety tags. This content is specified in the Circular No. 31/2014-BCT of the Ministry of Industry and Trade.
Making full use of labor protection made from insulating materials is a way to minimize accidents caused by electricity.
I. GENERAL CONTENT OF CIRCULAR NO. 31/2014-BCT
Subjects of application: This Circular applies to organizations and individuals that conduct electricity activities and use electricity on the territory of Vietnam, other relevant organizations and individuals.
Terms used in the Circular:
- Persons operating and repairing electricity in rural, mountainous, border or island areas are employees of electricity units operating under the Law on Cooperatives, operating in rural, mountainous or border areas. world and island.
- The operator, experiment, construction and repair of power lines or electrical equipment in an enterprise is an employee of the following units: Generation, transmission, distribution, construction, installation, use of electricity for manufacturing (with its own substation) operating under the Enterprise Law.
- The employer is the legal representative or authorized person of the organization, individual or unit directly managing the employee.
II. PROVISIONS OF THE CIRCULAR ON TRAINING FOR SAFETY, REPAYING AND GRANTING ELECTRIC SAFETY CARDS
The content of Circular No. 31/2014-BCT includes 6 chapters and 20 articles, in which the content of electricity safety training is specified in 6 articles of chapter II.
1. Article 4. Individuals given training, grade and card regarding electrical safety
1.1. Operators, testers, builders and repairmen for power lines and electrical equipment, including dispatchers and workers who install, remove, check and inspect electricity measurement systems.
1.2. Electrical operators and repairmen in rural and mountainous areas, border areas and islands.
2. Article 5. Theoretical training
2.1. General training
a) Electrical diagrams and requirements for electrical safety assurance
b) Safety assurance measures for works in progress: Conduct field surveys and make written records (if required), establish plans, register tasks, organize units, require assignment sheets or orders before performing tasks, abide by work permission procedures, supervise safety issues at work, conform to work completion procedures and switch on power.
c) Technical measures for preparation of safe workplace: Cut and prevent power from turning back on in work areas, check the presence of electric power, set up barriers, place warning boards and prohibition signs, and establish safe work zone.
d) Measures for identification and eradication of risks that may lead to problems and work accidents and methods for separation of electrocution victims from power source and first aid approaches
e) Features, effects, uses, maintenance methods, regulations on inspection (test) of safety equipment and work instruments commensurate with workers' assignments.
2.2. Specific training
a) Operators of transmission lines and electrical equipment
- For transmission lines:
+ Procedures for operation and handing of transmission lines’ issues;
+ Safety practice during: Examination of transmission lines, undertaking of live-line or off-line works, removal and trimming of plants in and near the protection barriers of transmission lines, work at height.
- For electrical equipment:
+ Operational procedures, problem handling procedures, safety procedures for electrical equipment and substations;
+ Safety practice during: Examination of electrical equipment, start or shutdown of electrical equipment, handling of electrical equipment and direct current systems;
+ Prevention and extinguishment of fire in electrical equipment and substations.
b) Electrical builders
- Safe practice during groundworks for electricity pylons and trenching work for underground electrical wires;
- Safety practice during installation and erection of pylons;
- Safe wiring practice for transmission lines and anti-lightning cords;
- Safe practice during installation of electrical equipment.
c) Electrical testers
- Operational procedures, problem handling procedures, safety procedures for apparatus of test stations and laboratories, test safety measures;
- Safe practice during separate tests for power generators, voltage and current transformers, electrical wires’ insulation.
d) Repairmen for transmission lines and electrical equipment
- For transmission lines: Safe practice during repair of transmission lines turned off, transmitting electricity in dependently or exposed to other live lines' effects;
- For electrical equipment: Safe practice upon handling of electrical equipment such as transformers, circuit breakers, power generators, high-voltage electric motors, capacitors, direct current systems.
e) Workers who install, remove, check and inspect electricity measurement systems on site
Safe practice during installation, removal, checking and inspection of offline and live-line electricity measurement systems on site.
3. Article 6. Practical training
1. Use, maintenance, examination and testing of safety equipment and work instruments commensurate with workers' assignments.
2. Methods for separation of electrocution victims from power source and first aid approaches.
3. Safe practices commensurate with workers' assignments.
4. Article 7. Organization of training
4.1. Employers shall bear the following responsibilities regarding workers as stated in Section 1, Article 4 of this Circular:
a) Prepare written materials and stipulate training schedule that correspond with workers’ safety grade and occupations;
b) Select trainers as per Section 3 of this Article;
c) Organize training, examinations, grading and issuance of cards regarding electrical safety for workers who have passed tests. If they fail tests in theory or practice, failed parts of the training must be re-taken;
d) Manage and supervise internal training, grading and issuance of cards regarding electrical safety.
4.2. Department of Industry and Trade shall bear the following responsibilities for workers as defined in Section 2, Article 4 of this Circular:
a) Prepare written materials and stipulate training schedule commensurate with safety grade and assignments of electrical operators and repairmen in rural and mountainous areas, border areas and islands;
b) Select trainers as per Section 3 of this Article;
c) Organize training, examinations, grading and issuance of cards regarding electrical safety for workers who have passed tests. If they fail tests in theory or practice, failed parts of the training must be re-taken at employers' requests.
4.3. Trainers
a) Theory trainers must possess university qualifications and at least 5 years’ expertise in specialist activities that they coach.
b) Practical trainers must possess at least college qualifications and 5 year’s work experience in specialist activities that they coach.
4.4. Form and duration of training
a) Initial training: It is given to new recruits. The duration of an initial training must be at least 24 hours.
b) Periodic training: It occurs on annual basis. The duration of a periodic training must be at least 8 hours.
c) Re-training: It is given to workers changing positions or safety grade, using new equipment or technology, failing tests or resuming after at least 6 months’ absence from work. The duration of a retraining must be at least 12 hours.
4.5. Depending on specific conditions:
Employers may organize separate electrical safety trainings, as the case may be, according to this Circular or combine trainings in work safety, work hygiene, fire fighting or other regulated drills.
4.6. Employers incur expenses of training and card issuance.
5. Article 8. Electrical safety grade
There shall be 5 grades of electrical safety, from 1/5 to 5/5.
5.1. Requirements on each electrical safety grade.
a) Grade 1/5:
- Accomplishment of at least 80% of the initial training in theory and practice;
- Possession of knowledge of general regulations for assurance of safety during performance of assignments;
- Compliance with regulations on use and management of safety equipment and work instruments provided.
b) Grade 2/5:
- Possession of knowledge of general regulations and safety measures for assurance of safety during performance of assignments;
- Compliance with regulations on use and management of safety equipment and work instruments provided;
- Possession of knowledge of methods for separation of electrocution victims from power source;
- Possession of knowledge of first-aid approaches for electrocution victims.
c) Grade 3/5:
- Similar requirements for grade 2/5;
- Possession of abilities to detect violations and unsafe behaviors;
- Possession of knowledge for examination and supervision of workers coping with power lines or electrical equipment.
d) Grade 4/5:
- Similar requirements for grade 3/5;
- Possession of thorough knowledge of responsibilities and work scope of each division joining in assignments;
- Possession of knowledge for safe practices and supervision of workers at work;
- Possession of abilities to analyze and investigate electrical problems and accidents.
đ) Grade 5/5:
- Similar requirements for grade 4/5;
- Possession of abilities to cooperate with other divisions, to give instructions, to organize safety measures and to inspect and supervise the performance of tasks.
5.2. Occupational eligibility by safety grade
a) Personnel graded 1/5 shall be eligible for:
- Assignments that require no contact with energized equipment or transmission lines;
- Provision of supports to divisions that cope with electrical equipment and transmission lines.
b) Personnel graded 2/5 shall be eligible for:
- Assignments given to holders of grade 1/5;
- Assignments in areas where electric power has been entirely cut.
c) Personnel graded 3/5 shall be eligible for:
- Assignments given to holders of grade 2/5;
- Assignments in areas where electric power has been partially cut;
- Live-line work with low-voltage lines and equipment;
- Performance of works on high-voltage power grids;
- Examination of substations and power lines in operation;
- Provision of work orders, direct instructions and permission to divisions and supervision of their working on low-voltage power grids.
c) Personnel graded 4/5 shall be eligible for:
- Assignments given to holders of grade 3/5;
- Live-line work with low-voltage and high-voltage lines and equipment;
- Provision of assignment sheets, work orders, direct instructions and permission to divisions and supervision of their working on transmission lines and electrical equipment.
dd) Personnel graded 5/5 shall fulfill all tasks assigned.
6. Article 9. Electrical safety card
6.1. Card issuance
a) New cards shall be issued to workers who have received initial training and passed tests or who change occupations.
b) Cards shall be reissued to workers who lost or damaged their cards.
c) Cards shall be revised and reissued to workers who change safety grade.
d) The time limit for issuance, re-issuance and revision of workers' cards as per Section 1, Article 4 of this Circular must not exceed 05 working days upon workers' accomplishment of initial training, periodic training, retraining and tests or upon their petitions for replacement of cards damaged or lost.
đ) The time limit for issuance, re-issuance and revision of workers' cards as per Section 2, Article 4 of this Circular must not exceed 10 working days upon workers' accomplishment of initial training, periodic training, retraining and tests or upon the Department of Industry and Trade’s receipt of their petitions for replacement of cards lost or damaged. Employers that employ workers as stated in Section 2, Article 4 of this Circular shall be responsible for submitting 01 application for training and card issuance to the Department of Industry and Trade by hand or by post. Such application includes:
- The employer’s letter of application that specifies: Full name, occupation and current safety grade of the workers;
- 02 portrait photos (2x3 cm) and previous electrical safety cards (if available) of the workers;
e) The sample card as per Appendix I in this Circular.
6.2. Usage
a) Term of validity: Upon issuance to the date of revocation.
b) Workers at work must carry and show electrical safety cards at requests of employers or electrical safety inspectors.
6.3. Revocation
a) Electrical safety cards shall be revoked upon workers’ transfer or discontinuation of employment.
b) Card issuers shall be responsible for card revocation
Electrical and mechanical engineering requires the constant remembering of electrical safety principles.
Above is the content of the Government regulations on training, ranking and granting electric safety card. Other contents such as the 2015 Law on Occupational Safety and Health, the revised Decree No. 44/2016 / ND-CP of the Government, the Circular No. 13/2016 / TT-BLĐ of the Ministry of Labor - Trade The Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs complements the regulations on occupational safety and sanitation in general.