6 types of substaions and how to decide which one to use | Galaxy M&E
In order for the project to effectively promote its efficiency, and to ensure adequate supply of applied electric power, it is necessary to be processed, designed, built and installed by units with expertise in the field of transformers.
We can see transformers used everywhere, from civil transformers used in electric fans to transformers used to stabilize voltage or used in electronic main boards.... One of the common applications is electricity. From small transformers to larger transformers with coils immersed in oil (oil is used to insulate and heat the steel sheets around the machine).
The effect of a machine or a substation is to transmit large electrical power from the place of production to the point of consumption. Transformers help minimize power capacity loss and aid the reduction of investment costs for power transmission lines.
Designing and constructing transformer stations are considered indispensable items for any industrial park, factory, and high-rise buildings these days. This is an important part of the heavy electrical system for electromechanical contractors. In order for organizations to envision an overview of the selection and use of transformers, this article will give 3 important headings, specifically as follows:
1. Classification of substations
The size of the substation depends on the amount of transmission capacity. The larger the scale, the higher the voltage. It is divided into 4 voltage levels:
Super high voltage: Greater than 500 kV
High voltage: 66 kV, 110 kV, 220 kV and 500 kV
Medium voltage: 6 kV, 10 kV, 15 kV, 22 kV and 35 kV
Low voltage: 0.4 kV, 0.2 kV and voltages less than 1 kV
Based on the voltage level, there are 2 ways to divide the substation:
Type 1: Intermediate transformer station that receives voltage from 220 kV to 35 kV and converts it to an output voltage of 15 kV - 35 kV according to demand.
Type 2: Workshop or distribution transformer stations receiving voltage of 6 kV to 35 kV, will be converted into an output voltage of 0.4 kV - 0.22 kV. This is a substation used in civil low-voltage networks, often used for buildings.
Commonly used transformers/substations are: 50, 75, 100, 160, 180, 250, 320, 400, 500, 560, 630, 750, 800, 1000, 1250, 1500, 1600, 1800, 2000, 2500 kVA.
2. Calculation and selection of substations
Organizations and individuals should consider 3 parameters to make specific requirements for consultancy units of mechanical and electrical engineering, design and construction:
Determine the load center and the location of the substation:
The first thing before designing, constructing and installing a transformer station is to calculate the load center and the location of the station to save wires which will minimize voltage drop and power loss of the electrical network. In addition, safety throughout the corridor including the electrical grid and the environment around it to make sure it doesn’t destroy the beauty which should be some factors to take into account when constructing it.
Determine the number of substations based on household classification
The number of transformers depend on the level of use, and the importance of the construction. It can be divided into 3 levels corresponding to 3 households using electricity.
Household type 1: Household type 1 are groups that affect human life or national security such as hospitals, clinics or headquarters of government agencies, agencies of the Ministry of Defense, etc. Class 1 households need to maintain a continuous power supply on the low-voltage line from the station, so two or more transformers are needed per station. Type 1 households use 2 transformers, each of which can withstand an overload of 1.4 times the capacity of the machine for 6 hours. Regarding economic issues, because the process of calculating transformer stations for households of type 1 often relies on the expected capacity, and the minimum load time could be less than the capacity of one transformer. Therefore, the operation process only needs to use 1 transformer for the whole load to avoid unnecessary power loss if using 2 machines.
Household type 2: Economic effect on the masses, such as factories, industrial parks, office buildings or places where people often gather (excluding public works). Category 2 households need at least 1 transformer per station.
Household type 3: Is usually family groups, or individuals. If this type of household is out of power, it will have less impact on the economy in general so it can be cut off for repair. Type 3 households often use one transformer at each power station. This typically occurs in residential areas.
Determination of substation capacity
There are many ways to calculate electrical capacity, of which there are 3 most commonly used currently:
Method 1: According to area and demand.
Method 2: According to the annual output of one product per 1 kW of electricity consumption.
Method 3: According to the installed capacity and demand factor based on the list of specific power consumption equipment that has been and will be a need.
3. Types of substations used
3.1. Outdoor substation
Outdoor stations are suitable for intermediate stations with high capacity because transformers, or large sized distribution equipment will be an appropriate choice to help save construction costs. Outdoor transformer stations include pad mounted substation (<3 × 75 kVA), gantry stations (<3 × 100 kVA), base stations (placed on concrete floors).
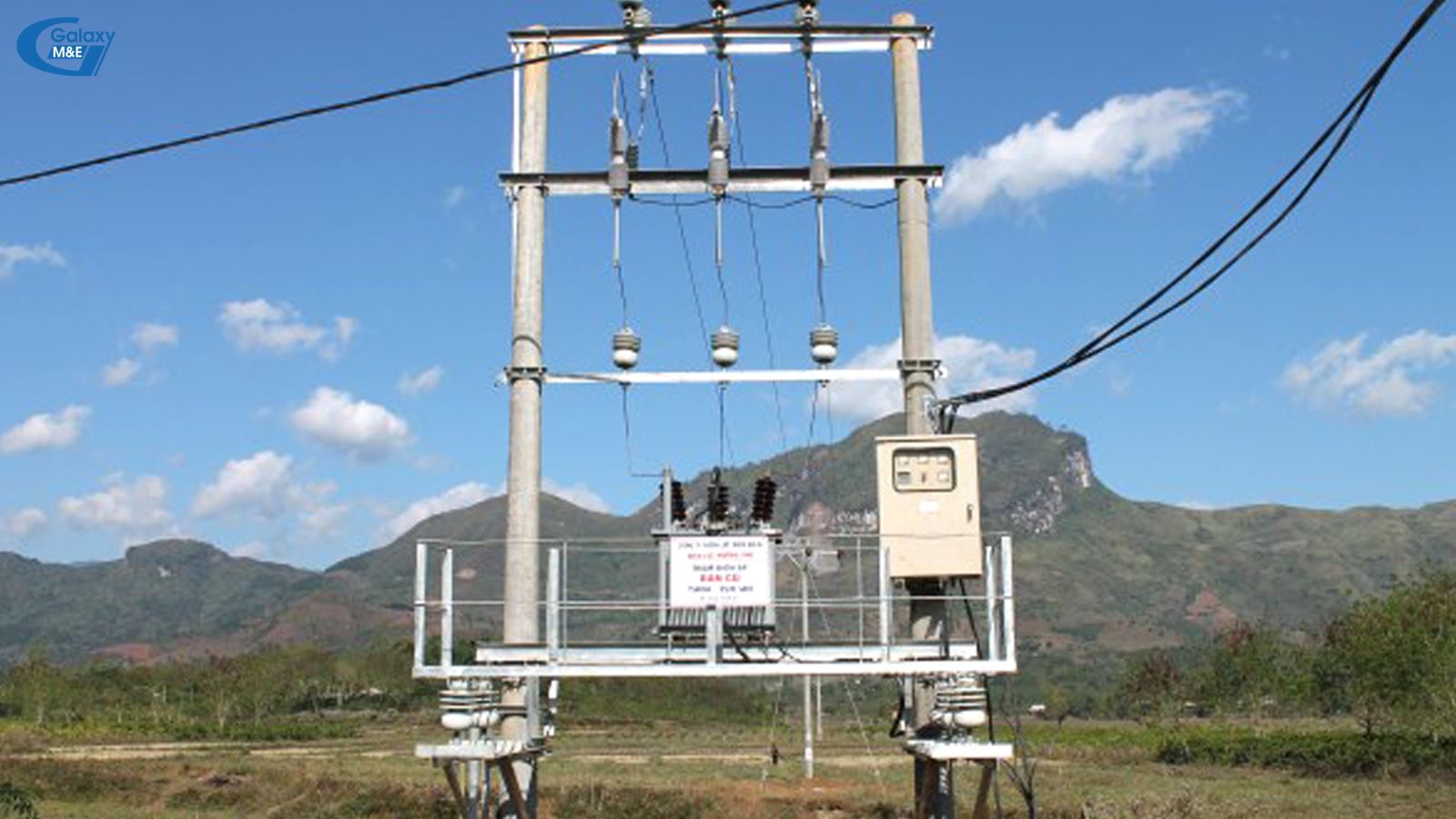
Hanging substation
Hanging substation:
A station where all high-voltage equipment and transformers are hung via poles. Transformers are usually single-phase or a combination of three single-phase transformers. Low voltage cabinet is placed on the column. This station usually saves space, so it is often used as a public station to provide for a residential area. Substation transformers are usually small (3 × 75 kVA), rated at 15 22 / 0.4 kV. However, this type of station often loses the beauty of the city, so in the long run this type of station is not recommended for urban use.

Gantry substation
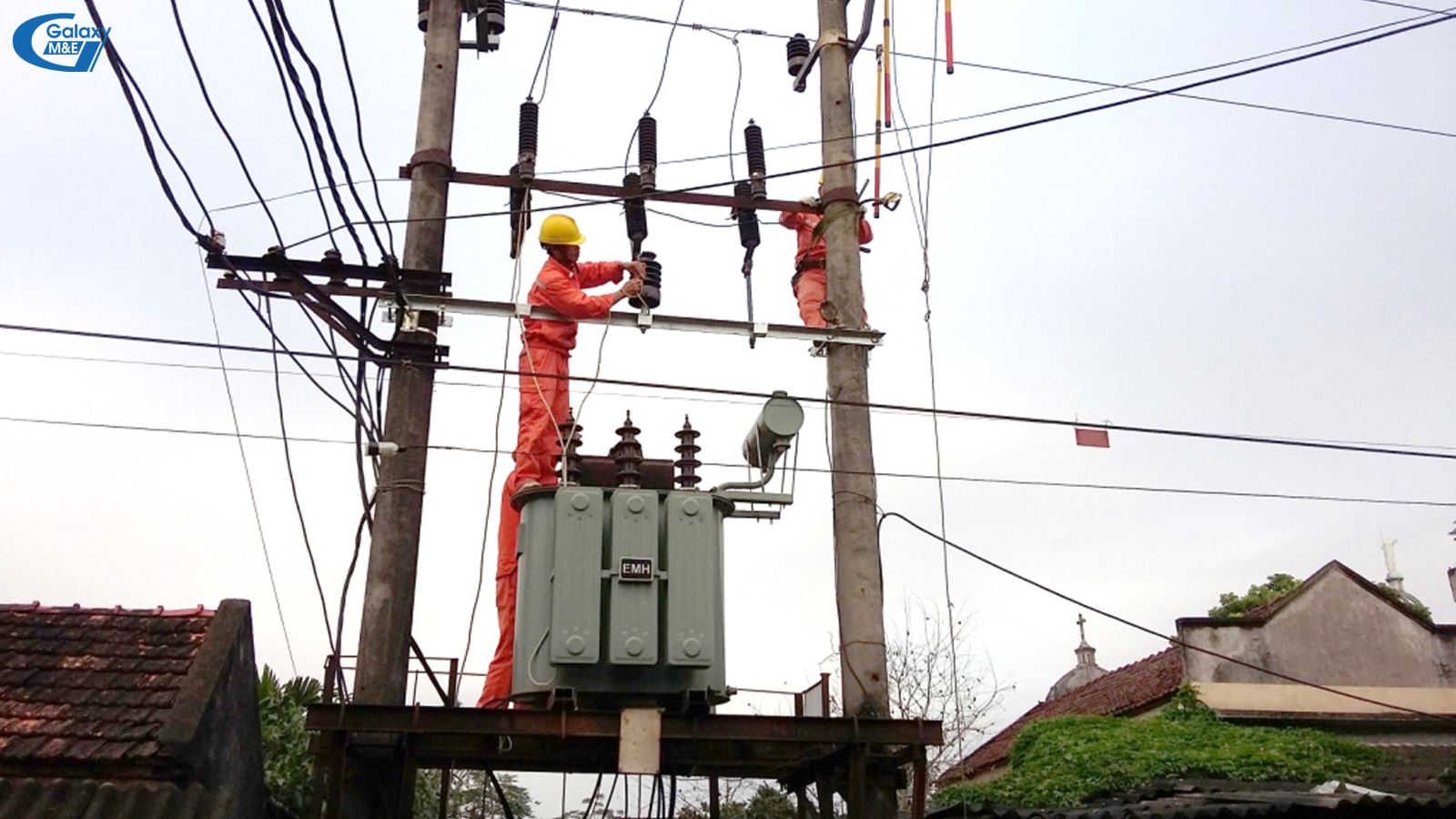
Gantry substation:
A gantry station is a type of station where all equipment and transformers are mounted on brackets between two columns. The station is equipped with three single-phase transformers (3 × 75 kVA) or a three-phase transformer (400 kVA), at a voltage of 15 22 kV / 0.4 kV. Measurement equipment can be located on the medium or lower side. Low voltage distribution cabinets are placed on the platform between two columns. The incoming line may be an overhead line or an underground cable. Gantry stations often supply electricity to residential areas or workshops.

Base substation
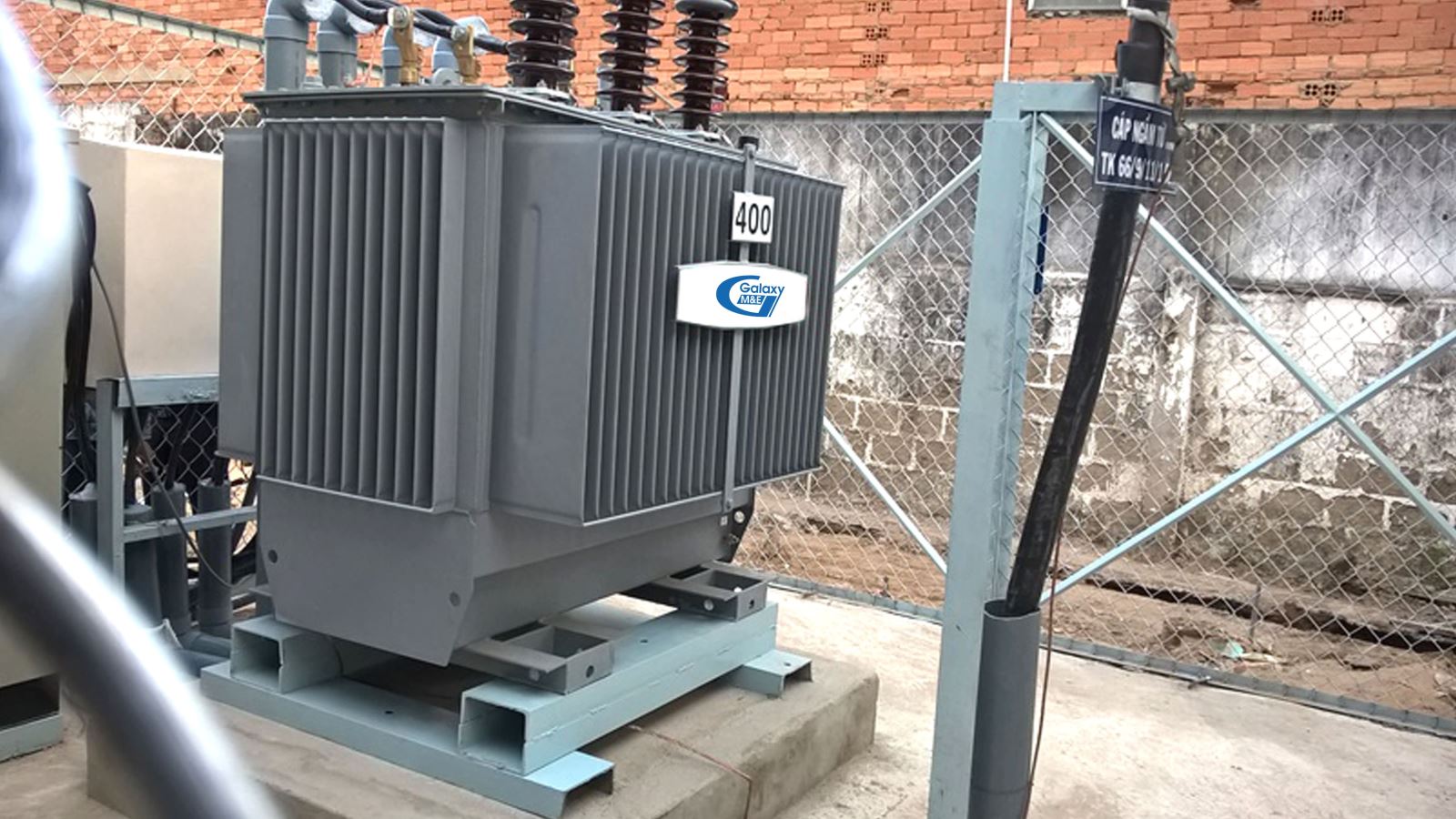
Base stations are often used in areas such as in rural areas, offices, small and medium-sized enterprises. For base stations, high-voltage equipment is mounted on poles, transformers are usually a group of three single-phase transformers or a three-phase transformer placed on the cement foundation on the ground and distribution cabinets are based in homes. Around the station there is a protective fence. The incoming line may be an underground cable or an overhead line. Measuring equipment is located in the medium or low pressure zone.
3.2. Indoor substation:
Indoor substations have the disadvantage of costly construction if using them requires large capacity. Due to the rough shape and texture, it is easy to cause architectural depreciation and damage. Besides the biggest disadvantage in cost, investors should not ignore the advantages of this type of station. Indoor substations are divided into 3 types:

Indoor substation
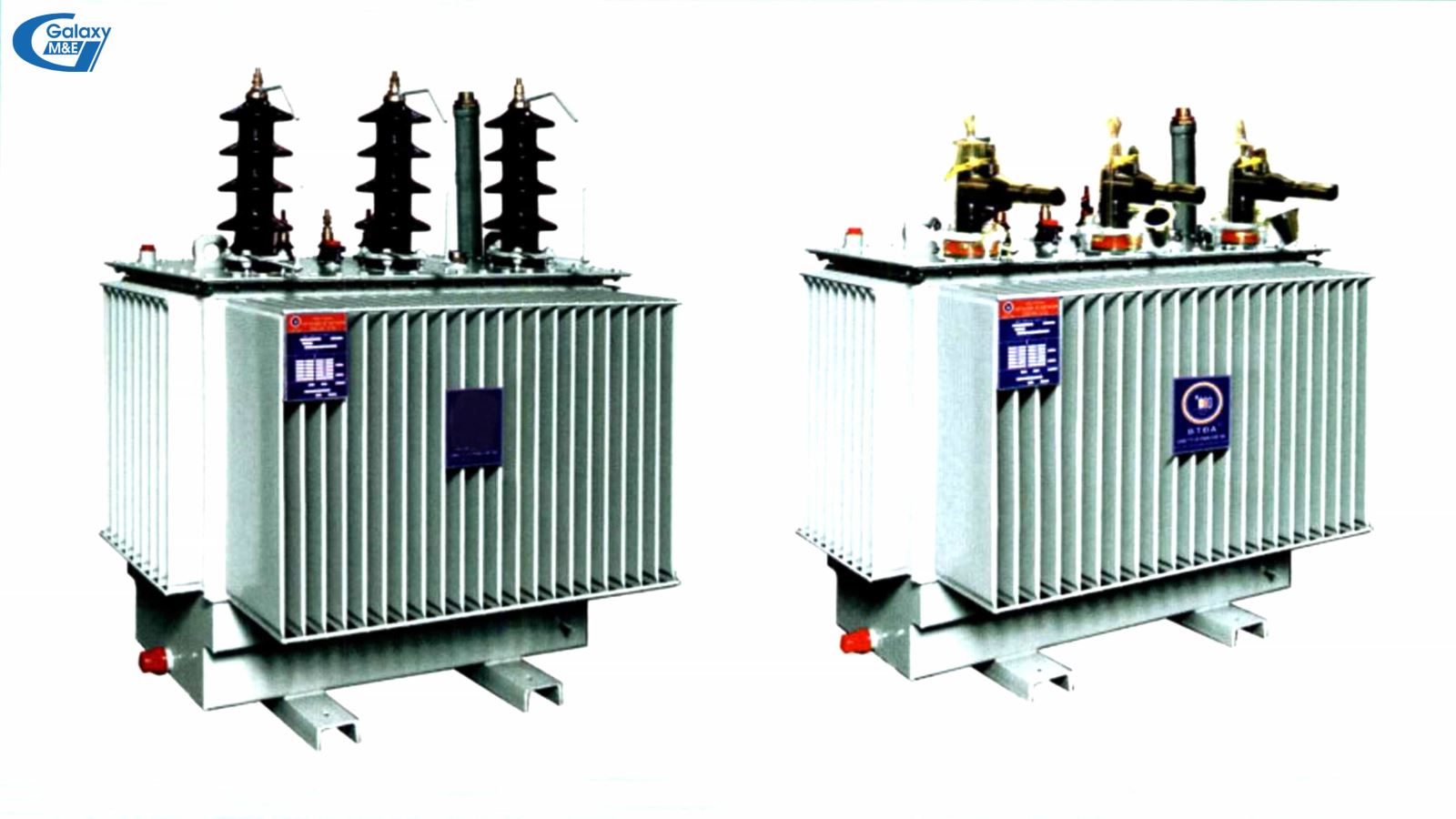
Closed substation:
Closed stations are types of stations where electrical equipment and transformers are located indoors. Closed stations are usually divided into public stations and customer stations.
- Public stations are usually located in new urban areas to ensure beauty and safety for users.
- Customer stations are usually located on customers' premises. The current trend is to use the main ring (Ring Main Unit) instead of the busbar structure, circuit breaker, and tube fuse is used to protect the transformer with a capacity of less than 1000 kVA.
For closed stations, the incoming and outgoing cables are usually underground. The vents have nets to prevent entry.

The complete substation was constructed and installed by Galaxy Electrical and Mechanical
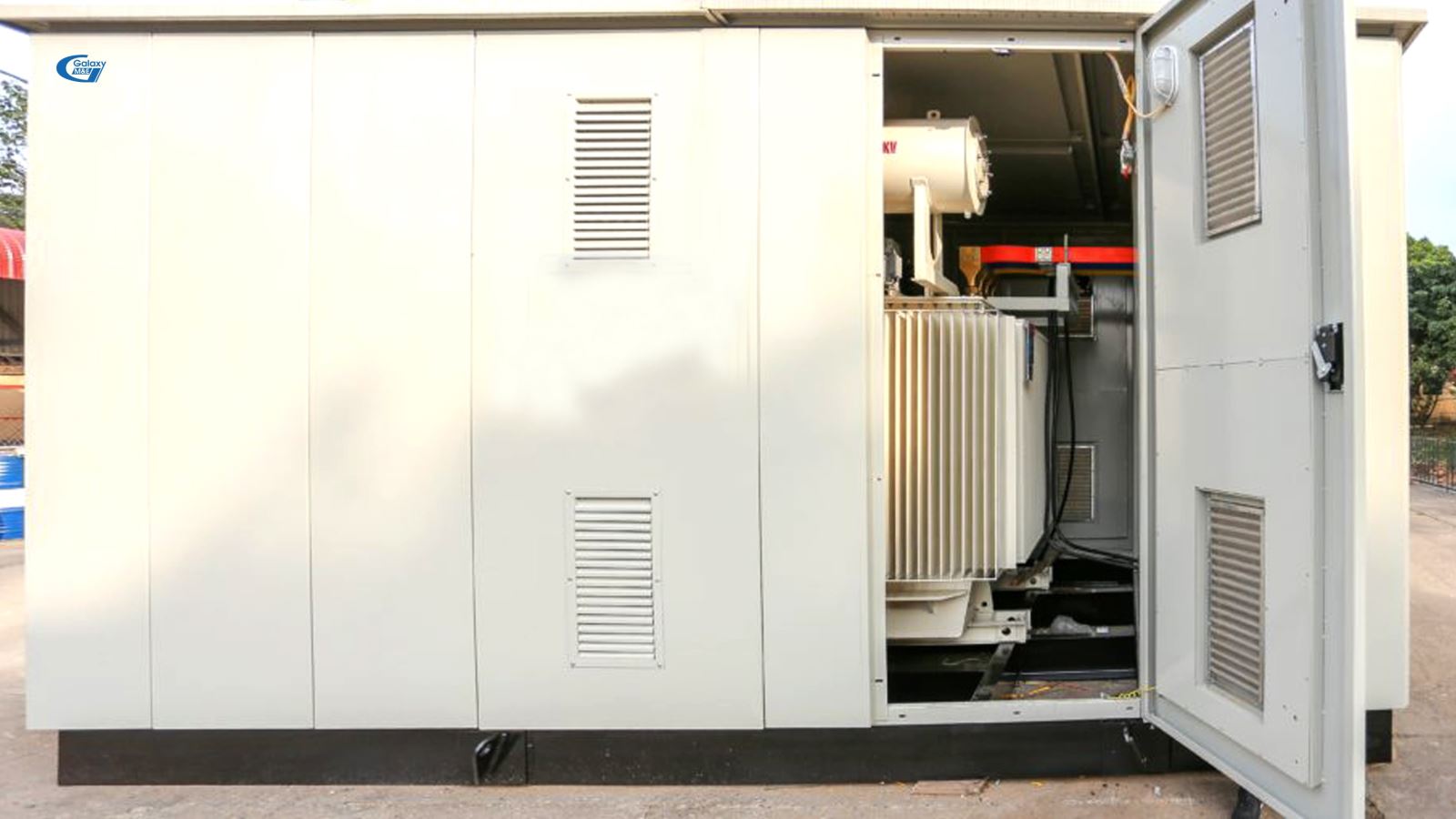
Complete substation:
For more complex stations that require the use of a ring-top power network structure or a switchboard containing many cutting, peeling, weather-proofing and impact-resistant devices, in these cases, they are considered a complete fully-enclosed stations. The station blocks are created and installed on concrete floors.
Because the appropriate choice from the type of installation; comply with all applicable international standards together with future standards; reduce research and design time, reduce installation costs; easy for synchronization and connection; tight texture. So the advantage of a full station is the optimization of materials and safety. Complete stations are often used in important places such as diplomatic offices, offices, hotels …
GIS switchgear is insulated by SF6 gas
GIS substation:
Gas Insulation Switchgear technology substations are stations that use SF6 gas-insulated switchgear. The characteristics of this type of station is that the area needs to construct it is several dozen times smaller than that of an outdoor station.
GIS stations are suitable for large cities, where there is a high demand for electricity consumption, where many important state agencies are located, and there is also a limited area for construction. In addition to the advantages of the construction area of the station, the GIS station uses gas-insulated switchgear, which does not expose to the environment to dust, GIS switch is very safe to operate, maintenance easier than those using traditional switchgear. GIS substations are the most technologically advanced today.
The above contents are not outside the purpose of supporting organizations and enterprises to gain more knowledge about designing, selecting and installing transformers and stations in general. In order for the project to be effective, and ensure adequate power supply to meet needs, it is necessary to consult or be consulted by units specialized in the field of electromechanical.
Galaxy M&E