How to capacity of air conditioning systems
For M&E contractors, the calculation of air conditioner capacity does not simply depend on the installation space.
The hot season is near. The demand for air conditioning installations will increase to meet the cooling needs of homes, offices and buildings in general. Although there are many pages / articles that share instructions on how to choose the air conditioner capacity, but when looking carefully, the content of these articles are still sketchy, subjective, and ignores many factors such as the external impact on the performance of air conditioning systems.
The following article of Galaxy M&E will help readers get sufficient information to choose the capacity of an air conditioning system that suits the needs and characteristics of space used.

What is the unit of air conditioning capacity? How to calculate the power consumption?
1. Unit of air conditioning capacity
To determine the cooling/heating capacity of an air conditioner, people usually rely on BTU. This is the British thermal unit, short for the British thermal unit. To determine the cooling capacity (W) of cooling / heating capacity, we take BTU parameter multiplied by 0.0002929. For example, an air conditioner has a rating of 12,000 BTU / h, so the cooling capacity will be 12,000 x 0,0002929 = 3,5148 kW. To determine the power consumption of the air conditioner, depending on the industrial or home appliance, we divide the cooling capacity (kW) with 3.2 or 2.8. For example, the cooling capacity is 3.5148 kW, after dividing by 2.8 we produce 1.2552 kW / h.
In addition to the BTU, people also use the HP index to measure harmonic power. HP stands for Horsepower.
1 HP equals 9,000 BTU, and corresponds to 745.7 W.

Improperly selected air-conditioning capacity is not only healthy but also wastes power and equipment procurement costs.
2. How to calculate the harmonic power
Choosing the right air conditioner capacity will help maintain room thermodynamics at a level suitable for the human body. The ideal temperature is 24oC and the humidity is 30-50%. Choosing an air conditioner with a large capacity that exceeds the space and demand will affect health, while wasting electricity. In contrast, using less capacity than space and demand also makes air conditioners operate continuously, both reducing equipment life, and also increasing power use.
One of the common ways to determine air conditioner capacity is by cooling / heating area. An air conditioner can be used for 2 rooms or 3 adjacent rooms (usually occurs with apartments). For the space of halls and meeting rooms with large areas, it is required to install multiple air conditioners or use central air conditioners at the same time.
After determining the area that needs cooling / heating, refer to the table below to temporarily calculate the BTU power level to be installed:
| Number | Area (m2) | Harmonic capacity |
| 1 | 9 - 5 | 9,000 |
| 2 | 15 - 20 | 12,000 |
| 3 | 20 - 30 | 18,000 |
| 4 | 30 - 40 | 24,000 |
| 5 | 40 - 50 | 30,000 |
| 6 | 50 - 60 | 36,000 |
| 7 | 60 - 70 | 42,000 |
| 8 | 80 - 90 | 48,000 |
| 9 | 90 - 110 | 60,000 |
Table of estimates of harmonic power corresponding to the space used.
3. Factors that cause M&E contractor to increase/decrease the air conditioner capacity
The table of reconciliation of harmonic power as mentioned above is only relative. In fact, with each space and different demand, the air conditioner capacity will increase / decrease.
The following factors will affect the performance of an air conditioner (Air Conditioner):
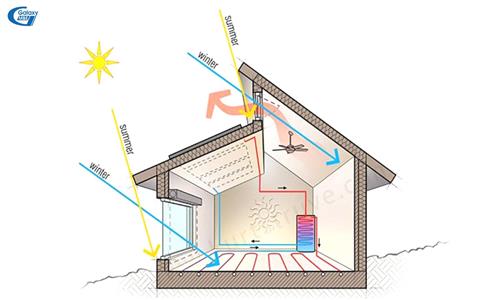
- Direction of the house: If the house is faced West, solar radiation will have a less of an impact on houses facing the East, South and North. The houses / buildings facing the south will keep the room temperature more balanced, warm in winter, cool in summer. Houses in the North and Northeast will be affected by cold air more than homes in the South.
- Construction materials: For steel frame houses, corrugated iron roofs, the absorption/heat dissipation will be greater than houses built with materials such as wood, cement ...
- Space structure: The more space is torn apart by the more walls, the less the working efficiency of the air conditioner. The more solidly enclosed walls are constructed (not applicable to materials with a higher thermal conductivity), the greater the cooling / heating efficiency. If you look at the houses built during the French colonial period, most of the walls are built of bricks and divided into two walls (inside and outside). The space between the two layers of wall forms a buffer, both serving heat transfer through the fireplace system and separating the hot air caused by summer.
- Number and size of doors used: The more doors a room has and / or the larger the size of the door is proportional to the heat dissipation.
- Number of users: The human body always emits heat. Therefore, if more people use the air conditioner in the same space, the cooling capacity of the air conditioner will decrease.
- Electrical equipment operating: Electrical equipment (Example: Light bulbs, computers, office equipment ...) when operating, they all generate heat energy. If more people use the air conditioner in the same space, the cooling capacity of the air conditioner will decrease.
- Space volume: The larger the volume of space, the less the cooling/heating capacity of the air conditioner.
To maximize the efficiency of the air conditioner, Galaxy M&E will help you to optimize the capacity with the following table:
| Number | Factors affecting harmonic capacity | Increase/decrease coefficient of expected air conditioner capacity |
| 1 | The area where the air conditioner is installed is facing north or northeast | 10% |
| 2 | The space is often exposed to sunlight or to the west | 10% |
| 3 | The space has poor insulation | 15% |
| 4 | The space has a kitchen (usually an apartment) or the total heat generated by electrical equipment is equivalent to the heat generated by a stove | 400 BTU/h |
| 5 | The space has 2 or more people regularly using air conditioning | 600 BTU/h |
| 6 | Air conditioner is only used at night | 30% |
| 7 | The harmonic capacity is calculated based on the space |
40 m3/HP |
Factors that increase/decrease the air conditioner capacity.
4. How electrical and mechanical contractors correctly determine air-conditioning capacity for office buildings, hotels and industrial workshops
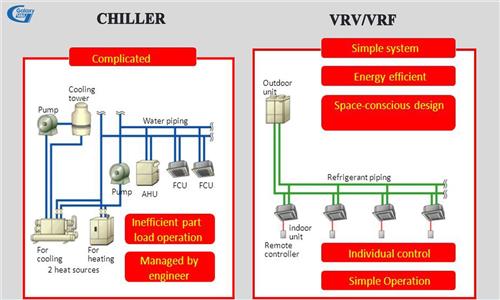
As mentioned in section 3, to determine the exact capacity of the air conditioner, it depends on the dependent variables (location of the building, number of users, operating machinery, construction materials ...). For large cooling/heating demands, most industrial buildings / workshops must use central air conditioning. Capacity and space characteristics are the factors to decide which system to choose: Either Chiller Water or VRV/VRF. Each air conditioning system and actual usage will have different costs. Therefore, to optimize investment costs, the calculation of air conditioner capacity is often assigned to Mechanical and Electrical consulting and construction units.
Thanks to the support of the software, the M&E companies will accurately calculate the amount of air conditioner capacity to install. Currently, some commonly used software types are Heatload Calculation, Trace 700, Trane ... However, before having enough parameters to enter as well as giving specific results, the M&E contractor must survey, measurement and professional use to identify the parameters affecting the performance of the air conditioning system.
Over time, each factory, building will change. The change may come from the retrofitting of machinery, increase / decrease of personnel, construction density around the building ... Each change in these factors will change the efficiency of using air conditioners. Optimize the installation capacity, increase equipment life, avoid waste, there's no other way the investor must consider but to choose a reputable electromechanical contractor. Experience and ability of the contractor will help maximize profits by choosing the appropriate air conditioning system.
Galaxy M&E