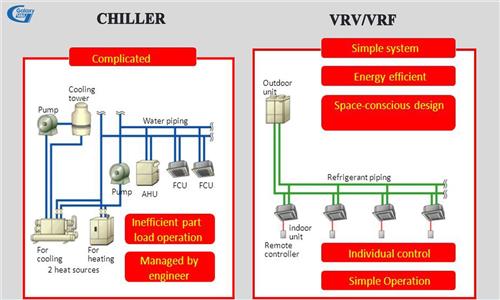
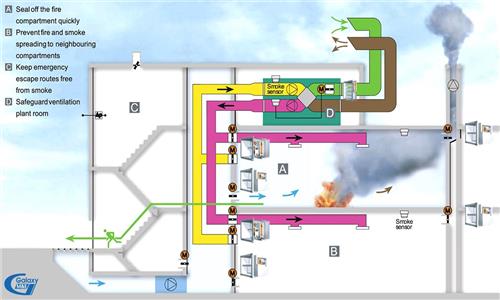
Factors affecting the air conditioning capacity in M&E works
In the M&E works, identifying and pushing all factors affecting the air-conditioner capacity will help investors reduce procurement costs and help aid the operation of air conditioning system.
The effect of air conditioning is to help control and adjust the temperature and humidity within a specific space. The cooling / heating capacity of an air conditioner is simply understood as the amount of heat that needs to be supplemented or removed by a regulating device. The heat is transferred from a hot environment to a cold environment, so in order to determine the exact capacity of the air conditioner to be installed, it is imperative to consider the factors that generate heat from inside and outside.

The location of buildings have a great influence on the choice of the air conditioning system.
1. Location of electromechanical construction works
The direction of a building or structure has a direct effect on the absorption of heat radiation. Following the sun's orbit, the south and west are more radiant than the east and north.
The location of the building is another important factor that affects heat absorption. The temperature of sunlight absorbed through the surface of the building depends on the location of the building on the earth's surface. The closer it is to the equator, the greater the amount of heat absorbed and vice versa. In addition, the surrounding space where the building exists also has an influence. If the location is surrounded by a lake or greenery system, the amount of heat absorbed will be reduced and limited compared to the location between buildings / construction. This explains why living spaces in rural areas are often cooler than in large urban areas.
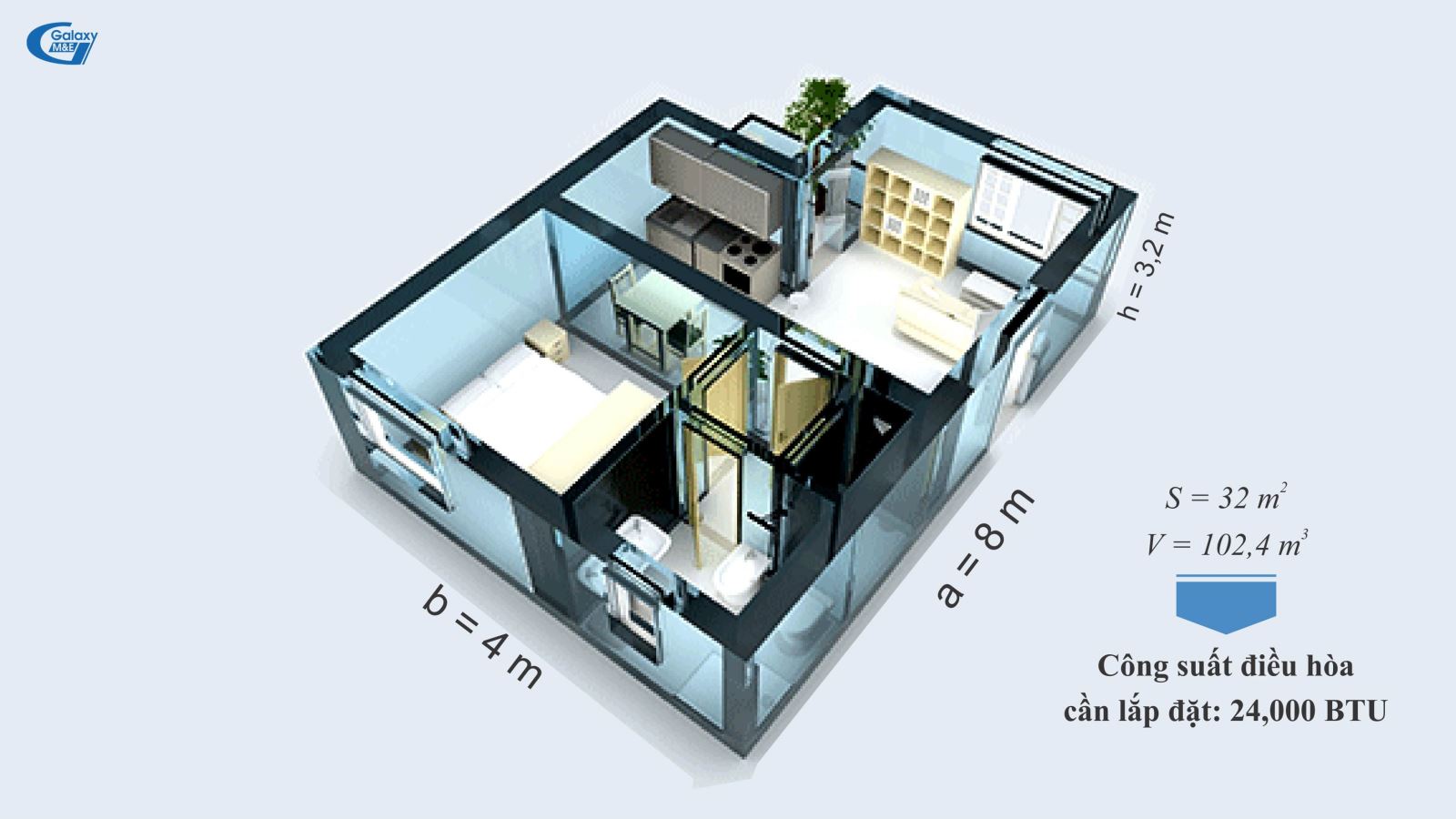
The bigger the space, the more the air conditioner needs to be used.
2. Physical dimensions of the construction space
The heat absorption of walls in air-conditioned spaces are directly proportional to the surface area. The higher the height of the ceiling, the greater the surface area of the walls. This also means that the air conditioner capacity must increase in proportion to the volume of space used. In addition, a space with too many counters, cabinets, shelves also means an increase in heat absorption. The same volume of space, the less cabinets/counters/ shelves, the less heat absorption will be achieved, while increasing the efficiency of the air-conditioning system.

Crowded places will need greater air conditioning capacity to offset the heat generated by individuals.
3. Amount of people in a specific space with an air conditioner.
The heat generated in the human body by oxidation, commonly known as metabolism. The rate of metabolism depends on the individual and the rate of activity. Under normal conditions, the human body will operate normally at a temperature of 37oC. With the heat created by metabolism, people also produce a certain amount of heat according to the work they are doing.
The amount of heat emitted by individuals are determined by the difference between the body surface and the surrounding space. For office work, the heat generated by a person is worth about 450 BTU / h. At home, when an individual is resting, the heat generated by an average person is approximately 300 BTU / h. According to this specification, a space for gathering 10 office workers will need a cooling capacity of 4,500 BTU. This capacity does not include energy for cooling spaces, lighting equipment, office machines.
Example of the need to increase the air conditioner capacity for the number of users:
If an area of 20 m2, ceiling height of 3 m, the air conditioner capacity is usually 12,000 BTU. If this space has 10 people working together, each person uses a laptop with a capacity of 65 W and a lamp with a capacity of 14 W, the total heat generated in 1 hour will be approximately 7196 BTU. Therefore, to compensate, one has to increase the air conditioner capacity from 12,000 BTU to 18,000 BTU (If the rooms window is facing North / Northeast) or 21,000 BTU (If the rooms window is facing West / West Northwest / West West) Male).

Conditioning capacity depends on the utility of each space.
4. Space utility uses air conditioning
Space utility using air conditioning is the function of the space corresponding to each specific operational needs. The stadium space with the main purpose of serving athletes and spectators will need greater air-conditioning capacity than the Opera space. Office space will need smaller air-conditioning capacity than the factory space. The space of a family room will need the same amount of air conditioner as a hotel room.
To explain more about the effect of space utilities on the air conditioner capacity to install, let's take an example of the calculation of the air conditioner capacity for an indoor gym. During the design of the Air Conditioning system, mechanical and electrical engineers will have to consider the following factors: the construction location of the gym, the spatial dimensions, the heat absorption generated by the structure and construction materials, number of spectators, ventilation systems, light doors, and electrical equipment used. In addition, because the characteristic of sports activities is that it always consumes and produces more heat than daily activities, the design of the air conditioning system requires engineers to consider the size of the gym. the number of athletes participating, the characteristics of consumption and heat emitted from each athlete, the activities before and after the competition process of the staff of the sports team.
In addition to the four influencing factors mentioned above, in order to increase cooling/heating efficiency, the M&E contractor may install additional ventilation systems to support air circulation, sharing heat in a space regulator using air conditioning. In addition, through the survey, the M&E contractor will also review and make the necessary recommendations to the investor to minimize heat loss, thereby adding data to the design and calculation air conditioner capacity is suitable for the project.
Galaxy M&E